
On the planet Earth, however, the situation is rather different. All other elements are present in relatively minuscule amounts, as far as we can detect. In the universe as a whole, the most common element is hydrogen (about 90%), followed by helium (most of the remaining 10%). (C) All of the elements that have been discovered are represented on the Periodic Table of Elements, which provides an elegant mechanism for not only displaying the elements, but describing many of their characteristics. Some examples of pure elements include (A) Bismuth, Bi, a heavy metal is used as a replacement for lead and in some medicines, like pepto-bismol, the antidiarrheal and (B) Strontium, Sr, a major component in fireworks.

For example, the symbol for sodium (Na) is derived from the latin word, natrium, which means sodium carbonate.įigure 2.1: Elements. These letter codes are derived from latin terminology. Some of the elements have seemingly strange letter codes, such as sodium which is Na. For example, the symbol for Hydrogen is H, and the symbol for carbon is C.
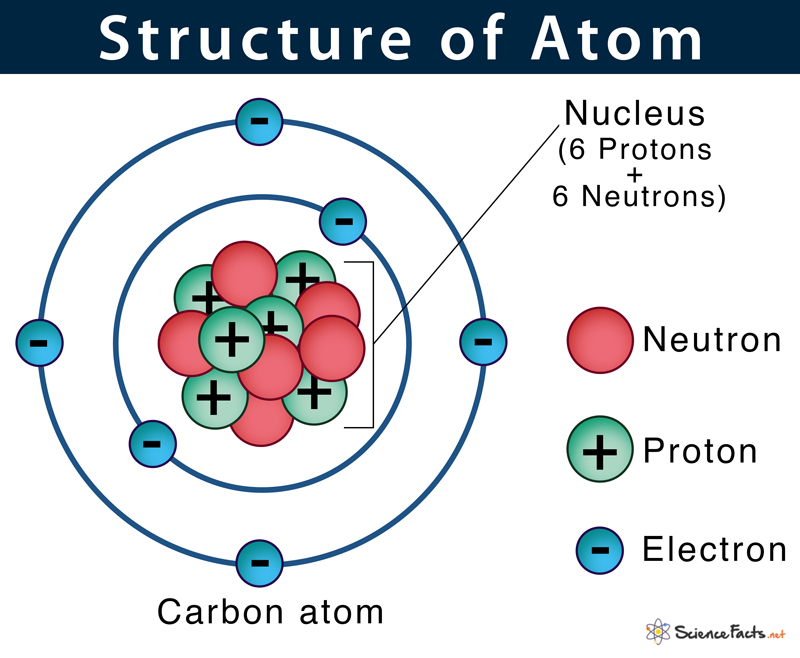
Each element is represented by a one or two letter code, where the first letter is always capitalized and, if a second letter is present, it is written in lowercase. Today, chemistry recognizes a total of 118 elements which are all represented on a standard chart of the elements, called the Periodic Table of Elements (Figure 2.1). Using technology, scientists have been able to create nearly 30 additional elements that are not readily found in nature. There are about 90 naturally occurring elements known on Earth. To begin our discussions of organic chemistry, we need to first take a look at chemical elements and understand how they interact to form chemical compounds.Ģ.2 Elements, Atoms, and the Periodic Table Elements and AbundanceĪn element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler chemical substances. The application of organic chemistry today can be seen everywhere you look, from the plastic making up components of your computer, to nylon which make up your clothes, to macromolecules and cells that make up your very body! Organic chemistry has expanded our world of knowledge and it is an essential part of the fields of medicine, biochemistry, biology, industry, nanotechnology, rocket science, and many more! It is the chemistry of life and includes all substances that have been derived from living systems. To put it simply, it is the study of all carbon-based compounds their structure, properties, and reactions and their use in synthesis. Organic chemistry is a growing subset of chemistry. Have you ever wondered why some plants can be used to make medicines while others are toxic and can kill you? Or why some foods are thought of as healthy while others are bad for you? Or how beverages like beer, cider and wine are made? This course is designed to introduce the reader to fundamental concepts in Organic Chemistry using consumer products, technologies and services as model systems to teach these core concepts and show how organic chemistry is an integrated part of everyday life. Sections: 2.1 What is Organic Chemistry? 2.2 Elements, Atoms, and the Periodic Table Elements and Abundance Atomic Theory Subatomic Particles Protons Determine the Identity of an Element Isotopes and Atomic Mass Electrons and the Periodic Table of the Elements Features of the Periodic Table 2.3 Chapter Summary 2.4 References This text is published under creative commons licensing, for referencing and adaptation, please click here.
Parts of an atom full#
For the interactive PDF, adobe reader is required for full functionality.
Parts of an atom pdf#
This content can also be downloaded as an printable PDF or an Interactive PDF.

Ch apter 2 – Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
